Hey there!🙋♀️ In this article I am going to help you getting general knowledge about COMPUTER (beneficial for the beginners). The computer is a fantastic device, and knowing how the computer works and how everything works together helps you get a better understanding of the computer.
WHAT IS COMPUTER? 🤔
A computer is a general purpose machine which consisting of digital circuitry, that accepts Input and generates Output.

FULL FORM OF COMPUTER?
- C = Commonly
- O = Operated
- M = Machine
- P = Particularly
- U = Used for
- T = Technical
- E = Education
- R = Research

5 COMPONENTS OF COMPUTER
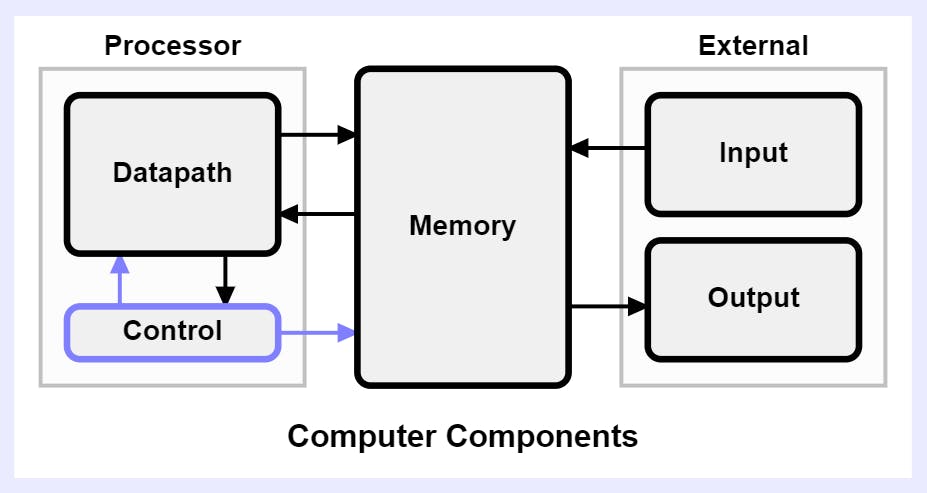
- Datapath - manipulates the data coming through the processor. It also provides a small amount of temporary data storage.
- Control - generates control signals that direct the operation of memory and the datapath.
- Memory - holds instructions and most of the data for currently executing programs.
- Input - external devices such as keyboards, mice, disks, and networks that provide input to the processor.
- Output - external devices such as displays, printers, disks, and networks that receive data from the processor.
TYPES OF COMPUTERS
Desktop computers
- Desktop computers design is made for use at a desk or table.
- They are typically larger and more powerful than other types of personal computers.
- The main component, called the system unit, is usually a rectangular case that sits on or underneath a desk.
- Other components, such as the monitor, mouse, and keyboard, connect to the system unit.
Laptops
- The Laptops are lightweight mobile PCs with a thin screen.
- Laptops can operate on batteries, so you can take them anywhere.
- Unlike desktops, laptops combine the CPU, screen, and keyboard in a single case.
- The screen folds down onto the keyboard when not in use.
Handheld computers (PDA)
- Handheld computers, also known as personal digital assistants (PDAs), are battery-power computers small enough to carry almost anywhere.
- These are useful for scheduling appointments, storing addresses and phone numbers, and playing games.
- Some have advanced capabilities, such as making telephone calls or accessing the Internet.
- Instead of keyboards, handheld computers have touch screens that you use with your finger.
GENERATION OF COMPUTERS
First Generation: (1940-1956)
- Vacuum tubes got use in circuits.
- These computers are very large in size.
- It requires a large amount of electricity.
- They produce more heat.
- They are less revival.
- Ex.: ENIAC, UNIVAC.

Second Generation: (1957-1962)
- Vacuum tubes got the replacement by transistors in circuits.
- Small size as compared to first Generation computers.
- Less amount of heat Generation.
- Less electricity consumption.
- Ex.: IBM 350
Third Generation: (1963-1972)
- Transistors got the replacement by I.C. in circuits. (I.C.- Integrated circuits)
- Small size as compared to second Generation computer.
- Less amount of heat as compared to second Generation computer.
- Less electricity consumption.
- Faster and more accurate than the second Generation computer.
- Ex.: IBM 360/370

Fourth Generation: (1973-Present)
- LSI and LSVI technologies are used.
- LSI- Large-scale integration.
- LSVI-Very large scale integration.
- Apple-II, STAR 1000

Fifth Generation: (Present & Beyond)
- It is based on the technique of Artificial Intelligence (AI).
- The computer can understand spoken words.
- Scientists are constantly working to increase the processing power of computers.
- They are trying to create a computer with real IQ with the help of advanced programming and technologies.
- Ex.: IBM Watson.

